AIS Cue (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry)

Lab instruments often used by practice and drilling are Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (AAS). AAS is a chemical analysis method used to measure the concentration of metals in samples.
AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry)
AAS stands for atomic absorption spectrophotometry, or spectrophotometry of atomic absorption in Indonesian language. AAS is an analysis method based on the process of absorbing radiation energy by atoms-atoms free in a fundamental state. AAS used to analyze metal content in a sample, whether it's heavy metals or light metals. AAS has a high quality of speciality and sensitivity.
The AAS principle of work is by extracting metal atoms in samples by using sunlight or lights, then observing the intensity of light received by detectors. The higher the concentration of metals in the sample, the greater the intensity of the light received by the detectors. In this way, the concentration of metals in samples can be measured very high.
AIR Cue of Work
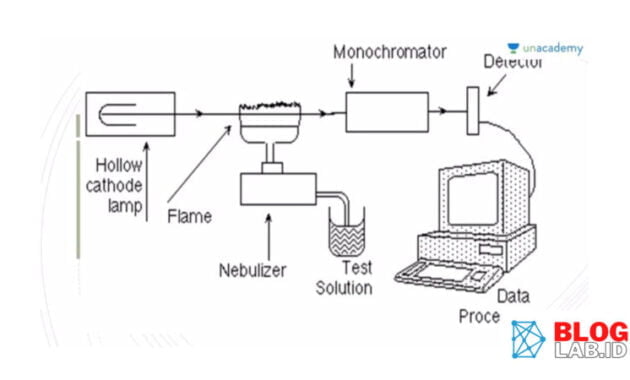
The AAS principle (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry) is to divide the molecular samples into atoms - atoms using fire or electricity. And then, atoms in the base can absorb light that is emitted by light sources, so it is excited.
The light that is not absorbed by the atom will be emitted by the detector and turn into a measured signal. The wavelength of light used depends on the electron array of an atom. The intensity of light measured depends on the number of atoms in a fundamental state.
The spectrophotometry of the atomic absorption is an analysis method based on the process of absorbing radiation energy from molecules at the most basic energy levels. This absorption stimulates electrons in the skin to be excited at a higher level of skin radiation. Each free atom has a unique wavelength, so absorption or radiation emissions occurs because of the movement of electrons from one level of atomic energy to another.
The AAS method is very specific because radiation absorption frequencies are characteristic of every element, so it barely has any interference.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry) is a chemical analysis method used to measure the concentration of metals in samples. The working principle is to break the molecular samples into atoms using fire or electricity, and then the atoms in the base can absorb the light that the light source emits, so it's excited. The signals produced from light that the atoms don't absorb will be emitted by detectors and measured. This method is very specific because radiation absorption frequencies are characteristic of every element, so it barely has any interference.