Oxygen and Reduction Understanding For example

Oxygen and reduction are two very common terms found in ilmu kimia. Both are associated with the role in the chemical reactions involving atoms, elements and compounds contained in chemicals. In a reaction of oxidation and reduction cannot be separated by electron delivery, acceptance and oxygen release and hydrogen, and change the number of oxidation.
Oxygen and Reduction
A brief oxidation is a process where a substance oxidizes another. Whereas reduction is a process where one substance reduces another. In a chemical reaction, these two processes are linked to oxidation that binds oxygen and reduction that brings it out.
However, it is certain that both oxidation and reduction in a chemical reaction can occur simultaneously. This process is called a reactive reaction.
Oxygen and Reduction Understanding
Here are some definitions of both:
- According to classical theory, oxidation is a process where a substance catches oxygen and loses hydrogen. Whereas reduction is a process where a substance loses oxygen and catches hydrogen. However, the concept of oxidation and reduction has evolved as research and experiment takes place. These two processes often abbreviate into a refractive reaction.
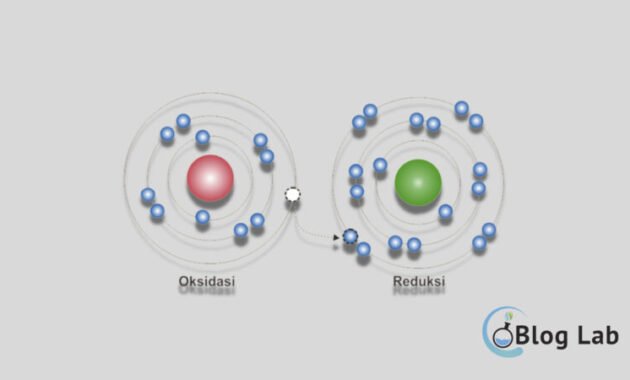
- According to modern theory, oxidation is a process where a substance loses one or more electrons. Therefore, the oxidation will become more positive. Whereas reduction is a process where a substance receives one or more electrons, so the cargo reduction becomes more negative.
The definition of these two theories is in line with a concept that explains the understanding of oxidation and reduction, which includes the transfer of electrons, change in oxidation numbers, and acceptance or oxygen release and hydrogen.
Moreover, the understanding of oxidation and reduction can also be seen as a change in the number of oxidation or what is known as bilocks. Reduction is defined as a reaction that causes the decline of the bilocks, while oxidation is defined as a reaction that causes the increase of the bilocks.
1. Oxygen Reduction Reaction (Reax)
The reactor process is divided into two parts, which is half reduced and half oxidized. These two processes always happen simultaneously, where half of them accept electrons and cause oxidation numbers to be reduced, while half of which are oxidized and cause oxidation to increase. A species that exchanges electrons to a refractive reaction is called oxidizing agents and induction agents.
The understanding of the level of equilibrium reaction can be determined by the electro-style analysis of galvanic cells. The state of equilibrium occurs when concentration reacts and products don't tend to change. The galvanic cell is a cell that appears spontaneously in a chemical reaction and can generate utilized electrical energy, which is measured in a voltage or potential cell unit.
2. Oxygen Enforcement Rule
The oxidation state of an element is related to the amount of electrons. Atom can lose, acquire or swap electrons when joining other atoms in a compound. There are seven rules used to determine oxidation, which is:
- Individual atomic oxidation state is zero (0).
- The total oxidation state of all atoms in the neutral species is 0 and on ions equals the ion charge.
- Section 1 has an oxidation rate + 1, the 2nd metal has an oxidation level + 2.
- Fluor oxidation state is -1 in a compound.
- Hydrogen usually has a + 1 oxidation value in the compound.
- Oxygen usually has a -2 oxidation value in the compound.
- In binary metal compounds, the element of group 17 has an oxidation state -1, the element of group 16 has an oxidation state -2, and the element of group 15 has an oxidation state -3.
Example Oxygen and Reduction
Here's an example and a kind
1. Combination reaction
The combination reaction is kind of the simplest reactive reaction, which involves merging elements into a Chemical compound. In the reactive reaction, both reduction and oxidation occur at the same time. The general equation used to describe the combination reaction:
A + B -> AB2. Parsing Reaction
Parsing reactions are also known as decomposition reactions. This reaction is contrary to the combination reaction, where the chemical compounds are broken up into separate elements that stand alone. Here's the equation:
AB -> A + B3. Single Replacement Reacts
The single reaction to a single replacement in chemistry involves "replacement" of the reactant element with other elements in the product. For example, we can see in the following equation:
A + BC -> AB + C
Four. Burner Replacement Reaction
Double replacement reactions are similar to single replacement. But in a double replacement reaction, two reactant elements are replaced with two elements in the product:
AB + CD -> AD + CB
5. Burning Reaction
The burning reaction always involves oxygen in the form of O2. The examples of burning reactions often found in everyday life are on light and heat.
CxHy + O2 -> CO2 +H2O
The burning reaction always involves a reactive reaction to chemicals oxidized by oxygen. There are many kinds of chemicals that can burn in the environment, for example titanium and magnesium that can burn in nitrogen. The same reaction that happens as follows:
2Ti + N2 (g) -> 2TiN
3Mg (s) + N2 (g) -? Mg3N2
There's also chemicals that can be oxidized other than using oxygen, for example, the Cl2 or the F2 reaction that both of them refer to as arson reactions.
Six. Disproportion reaction
The dispersal reaction is marked by a single substance that can be oxidized and reduced at the same time. The common equation used to describe the disproportion reaction is as follows:
2A -> A + n + A – n
At the equation reaction above, n is the number of electrons being transferred. The disproportion reaction can occur without a neutral molecule that becomes the initial reaction. This reaction also involves more than two chemical species but with a different level of oxidation.
Oxygen and Reduction empowerment
The reactive reaction that combined reduction and oxidation is often used in industrial processes. The regular industry implements this reaction among other metal processing industries, metal bonding industries, as well as the battery industry and batteries.
Here's an explanation on each industry:
1. Metal Processing
Metal seeds can be found in many forms such as oxide, carbonate, and sulfide. The seeds of carbonate and sulfide must first be processed into oxide through the grill process. After that, the oxide seeds will be reduced to metal through appropriate processes.
2. Metal Processing
It's done by oxidizing the metal to be coated, then reduces the desired elements and attaches them to the desired metals. The goal is to increase the metal quality, such as preventing the iron from being coated with zinc or chrome, or in copper with gold lining.
3. Aki and Battery
Aki and batteries used in everyday life play an important role as a direct power source. The working principles of the battery and battery are based on a reactive reaction.
Conclusion
It can be said that oxidation in a chemical reaction involves interaction between oxygen and other substances, which leads to oxygen bonding, electron release, and increasing numbers of oxidation. Instead, reduction pertains to oxygen release, electron capture, and oxygen dropping numbers. Oxygen can have positive effects such as the long-lasting form of aluminum, but it can also be as harmful as with iron grafts or the discoloration of cut fruit.
That's an article we can present to readers about understanding oxidation and reduction, reactions, rules, and examples of applications in daily life. May it give a good understanding to all who need it.